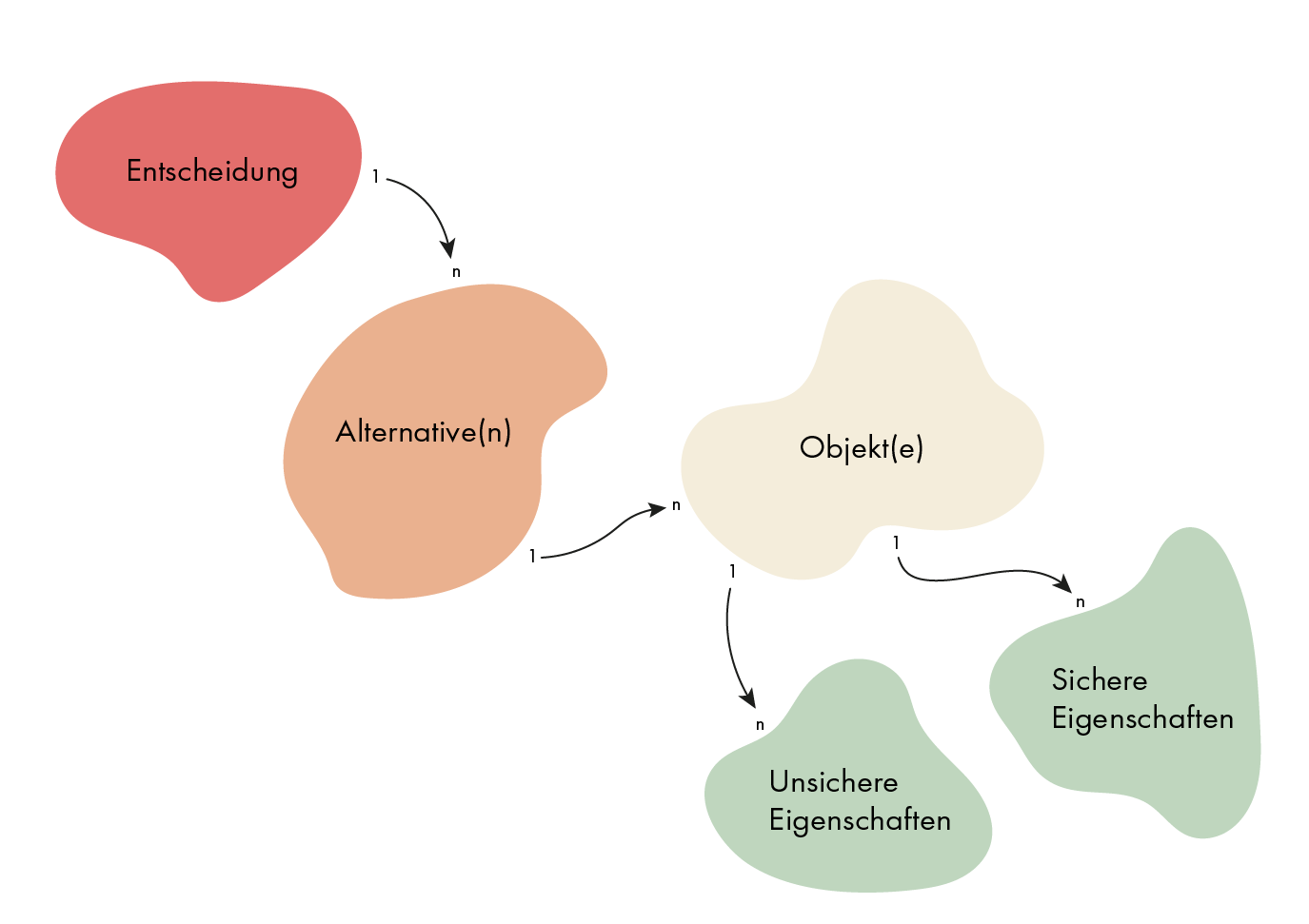
The process is basically the same for both methods. Only the information gathering and thus the generation of alternatives is different. The best alternative is then selected using one of the following techniques. This list is far from complete and error-free. There is a long, scientific history on decision theory under security, risk and uncertainty. With the following terminology, it becomes clear that the difficulty in selecting the best alternative depends not only on the decision maker, but also on the decision object. This is because a decision object can have several properties at the same time and these can also be uncertain, i.e. have probabilities.

A classic example comes from the world of finance: when you are considering which share to invest in, that share has, among other things
and while the first property is defined (it is legally determined whether and if so which voting right the share holder has), the other two are stochastic in nature and also correlate with each other! So it is not easy to make the right choice between ten different shares!
But this also applies to seemingly more banal decisions. Imagine you want to surprise someone and are now looking for which restaurant to go to tonight. The restaurants are the alternatives. Each alternative now has several objects, for example:
And each of these objects has several properties. For example, the location has
And the cuisine has the features
You see - it is not easy, even if you have to make a decision on your own.
Procedures (also called techniques/practices):